- Home
- Email Header Analyzer
Learn How to Perform Email Header Investigation
Email is the most significant application on Internet for messages communication, documents delivery, and carrying out transactions. It is not only used on PC but on various electronic gadgets like mobile phones makes easy to access the emails. With the increase in the criminal activities, there is a continuous misuse of emails for illegal purposes by phishing emails, sending spam, distributing child pornography, and hate emails besides spreading viruses, hoaxes, worms, and Trojan horses. Further, Internet infrastructure misuse via DOS, waste of storage space and computational resources are costing every Internet user whether directly or indirectly. It is thus an essential to identify as well as eliminate users who are misusing email service. Email Header Investigation is utilized for studying the source and content of email message as evidence and for identifying the actual sender, recipient along with all its details. In the following section, we will discuss the deep way for reading, view an email header and email header analysis. And find how to analysis of email header and how to reduce chances of emails phishing.
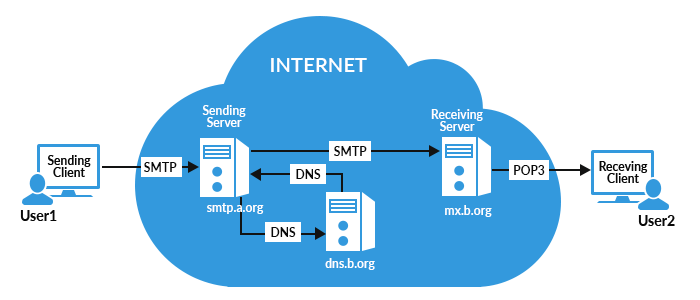
Analysis of Email Header
Emails are the highly distributed service that involves various services to accomplish end-to-end email exchange. These services come under various factors that are mentioned below:
User Services Type
User Services type include the organizations, people, or processes, who serve as sources or sinks of messages. They can create, modify, or look at the complete message. These can be of four types as mentioned:
Sender: The sender is the one who is responsible for generating the message, its contents, as well as its list of Recipient addresses. The MHS transfers the mail from the sender and delivers it to the receiver. The MHS plays an Originator role, which correlates with the Sender role.
Receiver: The Receiver is a consumer to whom the message is delivered. The MHS has a Receiver role that correlates with the Recipient role. A Recipient can close the user-communication loop by making and submitting a new mail that replies to the Author.
Return Handler: It is a special form of Recipient, which gives the notifications of failures or completions that are generated by the MHS as it transmissions or delivers the message. It is also known as Bounce Handler.
Mediator: It receives, reformulates, aggregates, and redistributes the messages among Authors as well as Recipients. It forwards a message via a re-posting procedure. It shares some functionality with simple MTA relaying however, it has more flexibility in both addressing as well as content than available to MTAs. It protects the integrity and original message that contains the essential aspects of its origination information. It might also add commentary. It does not make a new message, which forwards an annotation existing message, or Reply.
Message Handling Service (MHS)
Actors are responsible for end-to-end transmission of messages. These Actors can create, modify, or look at transferal data in the message. MHS Actors can be of following four types.
Originator: It safeguards that a message is valid for posting and then submits it to a Relay. It is responsible for the Mail Submission Agent functions. It also makes any post-submission that concern for sending error and delivery notice. The Author makes the message, but the Originator handles any transmission issues with it.
Relay: It makes MHS-level transfer-service routing and save-and-forward function by transmitting or retransmitting the message to its receiver. It enhances trace information but it does not modify the information, which is an envelope or the semantics of message content. It can adjust message content representation, such as changing the form of encoding transfer from binary to text, but only) to meet the capabilities of the next hop in the MHS. When a Relay stops attempting for transfer of a message, it becomes an Author as it sends an error message to the Return Address.
Gateway: It attaches heterogeneous mail services instead of differences in their syntax and semantics. It can also send a required message to a Recipient on the other side, without needing changes to any components in the Author's as well as Recipient's services of mail.
Receiver: It makes final delivery or sends a message to an alternate address. It can also perform filtering as well as other policy enforcement immediately before or after delivery of mail.
Administrative Management Domain (ADMD)
Actors that related with different organizations have their own operating policies, administrative authority, as well as trust-based decision-making. Its Actors can be of following three types:
Edge: It is a service of independent transfer in networks at the edge of an open Internet Mail service.
Consumer: Its influence a type of Edge service, as it is common for web-based email access.
Transit: Email Service Providers (ESPs), which give value-added capabilities for Edge ADMDs, such as aggregation as well as filtering.
Conclusion
In the present arena, most of the crimes are done via email it's important to analysis of email header every time whenever emails receive. After understanding the same thing, we have discussed deep email header investigation and how to view an email header. It helps users to understand completely that email header not only contains what it shows to us instead it contains deep more. Secure emails with email header analysis tool.
